افشین رشید
اُستادیار ؛ عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی واحد علوم و تحقیقات تهران
654 یادداشت منتشر شدهThe Manufacture of Nanotubes is Very important in The Production, Propagation, and improvement of Nanotransistors.
Note: Nanotube fabrication is very important in the production, propagation, and enhancement of nanotransistors. The most important difference between gas-based and solid-source methods for nanotube fabrication is that CCVD typically uses low temperatures and grows nanotubes at temperatures below 0.111 degrees.
More than one mechanism can be involved in the growth of carbon nanotubes, depending on the type of gaseous precursors, the catalyst used, and the operating parameters. The dissolution-infiltration-deposition mechanism is the most common one, which is mostly prevalent in low-temperature methods. In this mechanism, catalytic nanoparticles of metal alloys or transition metals (such as nickel, iron, and cobalt) are considered spherical or floating on the surface of the substrate . When hydrocarbon vapor (such as CO, CH4, C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6) comes into contact with hot catalyst particles, it decomposes into carbon and hydrogen, and carbon infiltrates the substrate metal. When the carbon atoms in the catalyst reach a supersaturation level, the precipitation and growth of carbon nanotubes begins.
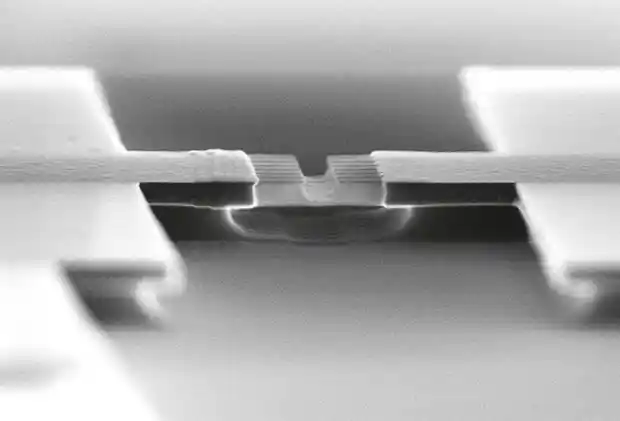
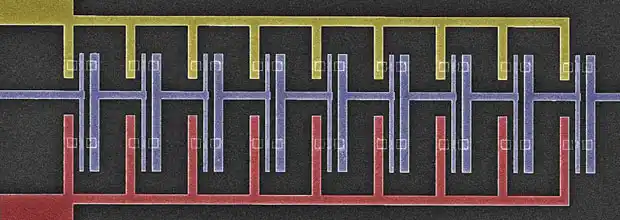
If the interaction of the catalyst with the substrate is weak, the metal with the substrate has an acute contact angle (nanotube at the bottom of the catalyst) (tip growth) and if the interaction of the catalyst with the substrate is strong, the metal with the substrate has an open contact angle, the nanotube grows above the catalyst (growth base). In the first case, it is possible to produce a nanotube with one open end. The physical form of the deposited carbon, single-walled, multi-walled, amorphous carbon nanotubes and the graphite layer covering the catalyst nanoparticles depends on many factors such as the size of the catalyst particles and the deposition rate. When the deposition rate is equal to or less than the carbon diffusion rate, a graphite layer is formed around the catalytic nanoparticles. When the deposition rate is greater than the carbon diffusion rate, a carbon nanotube is formed. The size of the catalytic nanoparticles plays an important role in the growth of nanotubes. Generally, small-sized catalytic nanoparticles (less than 0.1 nm) are active for the nucleation and growth of carbon nanotubes. If the particle size is within one nanometer, a single-walled nanotube is formed. Catalytic nanoparticles with a size of 0.1 to 51 nm lead to the growth of multi-walled nanotubes. Catalytic nanoparticles with a size larger than 51 nm are also covered with amorphous graphite sheets. Graphene has wide applications in the field of electronics due to some unique physical properties. Among these properties, the mobility of charged particles within graphene, or the mobility represented by the letter μ, is very important. The mobility value for graphene is 100,000 sV/cm2, and the saturation velocity for it has been reported to be about 5×107 s/m. The sum of these properties makes graphene a strong conductor for electronic applications, including use in transistors. In the production and propagation of tubular nanotransistors, the methods for producing carbon nanotubes are divided into two general categories: methods based on solid and gas carbon sources. Generally, CCVD methods use lower temperatures to produce carbon nanotubes compared to solid carbon sources. Understanding the mechanism of carbon nanotube production in order to optimize its characteristics is a very important approach in the production of nanotransistors. Many parameters such as crystal particle size, substrate type and deposition rate are involved in these mechanisms. The size of the catalyst is one of the important factors affecting the characteristics of the produced carbon nanotubes and by changing it, multi-walled and single-walled carbon nanotubes can be produced. Some methods such as electric arc and mold have the ability to produce carbon nanotubes in the absence of a catalyst, which leads to the production of products with higher purity.
Conclusion :
The fabrication of nanotubes is very important in the production, propagation, and enhancement of nanotransistors. The most important difference between gas-based and solid-source methods for the fabrication of nanotubes is that in CCVD, low temperatures are usually used, and nanotubes grow at temperatures below 0.111 degrees.