افشین رشید
اُستادیار ؛ عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی واحد علوم و تحقیقات تهران
654 یادداشت منتشر شده_ Simulation process section in (Electrical Nanoparticles) Changing the chemical structure and the effect of reaction temperature on the size and structure of nanoparticles Nano particle
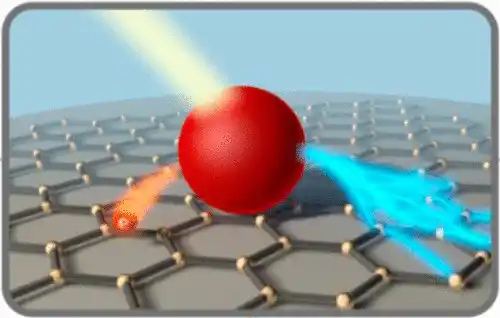
Note: The effect of reaction temperature on nanoparticle size. Reaction temperature is a variable factor in determining size, and particle size distribution plays a significant role. An appropriate reaction temperature produces nanocrystals with a narrow size.
At such temperatures, the nucleation and growth stages occur separately and can even delay the start of the growth stage, so that it occurs after the formation of nuclei. In general, increasing the reaction temperature increases the rate of the reduction reaction. However, regarding the effects of temperature on the size of the nanoparticles and the optimal temperature for the production of electrochemical nanoparticles by the chemical reduction method, it was experimentally obtained for various production conditions. In the case of the synthesis of nanoparticles by the chemical reduction method, with increasing the reaction temperature, the size of the electrochemical nanoparticles increased and non-uniform particles were obtained. This behavior occurs at lower temperatures, the growth rate of the nuclei is lower and the size of the produced particles is smaller, and the uniformity of the particles is more required. The effects of temperature on the chemical reduction of nanomaterials and the effect on electrochemical particles are investigated, as temperature has a significant effect on the shape, size and morphology of the nanoparticles. At low temperatures (zero degrees), the reaction rate is very low and the process of completing the reduction reaction takes hours. At temperatures between 10 and 55 degrees Celsius, as the temperature increases, the rate of the addition reaction decreases and the size of the particles produced also increases.

With increasing reaction temperature, the size of the produced particles decreased. The phenomenon of increasing the nucleation time is proportional to the increase in temperature, which causes a decrease in the size of the produced particles. The size of the nanoparticles produced at 09 degrees Celsius is smaller than that produced at 59 degrees Celsius . The effect of reaction time on the size of the nanoparticles Reaction time is also an important parameter in controlling the size and shape of the final product. Reaction strategy In the early stages of growth, smaller electrochemical nanoparticles can be obtained. The strategy harms the overall efficiency of the reaction, because the monitoring material in this case is partially converted into electrochemical nanoparticles. When the precursor is added to the reaction solution, nucleation immediately begins and small nanocrystals are formed, which causes a noticeable change in the color of the solution. Over time, the nuclei produced stick together and form larger particles.
However, as the reaction time increases, more ions are reduced to the electrochemical nano-form and the nanoparticles become larger. From there, the particles become reduced and only the size of the particles increases. Therefore , a trade-off between reaction efficiency and particle size is necessary to achieve the electrochemical reaction within the reaction time. Also, with increasing reaction time , the shape and size of the produced particles become more uniform.
Conclusion :
Effect of reaction temperature on nanoparticle size Reaction temperature is a variable determinant of size, and particle size distribution plays a significant role. An appropriate reaction temperature produces nanocrystals with a narrow size.