افشین رشید
اُستادیار ؛ عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی واحد علوم و تحقیقات تهران
657 یادداشت منتشر شدهGetting to know more and introducing different components and units of microcontrollers

Note: Different parts of the microcontroller are each intended for a specific application. An electronic designer uses different parts according to his needs in the project. For this purpose, it is enough to activate the required settings in the desired section. By choosing a suitable microcontroller, we can implement simple electronic projects by saving the number of digital ICs. The advantage of this method is the high speed of the circuit and its cost-effectiveness.
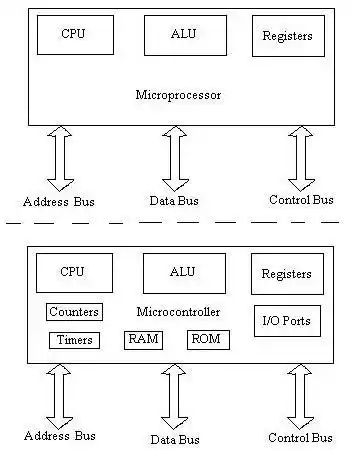
This microcontroller is available in three types of packages. Its two models are SMD type and its simple type with two rows packaging (DIP). The DIP type microcontroller is better placed on the board. This type of microcontroller ICs are used more often. A microcontroller is a programmable device. It means that the work method can be defined according to the need for this part in the form of a program. In order to be able to define the idea and method of work execution for the microcontroller in such a way that it can execute the work process accurately. This compact microcomputer (microcontroller) consists of the following different parts.
RAM temporary memory: In this memory, the program and a part of the data (Data) are temporarily executed and stored temporarily until the microcontroller is connected to the electric current.
Readable ROM memory: This memory is used to locate the required program and data that is fixed . This data includes a table of fixed data that is used to display characters and special shapes on the seven-segment display (Seg 7) connected to the microcontroller. Today, in microcontrollers, the family of Flash RAM (RAM Flash Cooldisk) is used. EEPROM memories are also used if there is a need to store stable data without the need for power during the program execution process . In this case, when the power is cut off, the information stored in the microcontroller will not be lost.
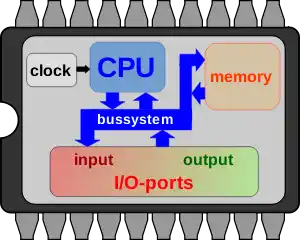
Central processing unit - CPU: means processor and is considered the main and central unit (brain) of the microcontroller. The processor consists of calculation, logic, main registers, and a unit for receiving and translating program codes. The greater the coordination of these parts, the faster the processing, these types of microcontrollers are called high-speed microcontrollers.
Digital input and output - O/I DIGITAL: This section includes the set of input and output bases of the microcontroller, the function of these bases can be defined through the commands compiled in programming. In this way, we can assign different data to the input or output and create different modes.
Clock: In this section, a square wave is produced as a clock pulse. This pulse is required by the microcontroller, which, for example, can be produced in the following two ways.
Internal RC mode: the clock pulse is generated inside the microcontroller IC.
External crystal mode: The clock pulse is produced by installing a piezoelectric crystal to the microcontroller bases. In most applications, the internal RC mode is used, because it no longer needs an external part to connect to the microcontroller.
When a project is to be done with microcontrollers, after determining the purpose of the project and its cost-effectiveness, the stages of hardware design, software design, algorithm or flowchart, programming, simulation and program implementation must be done. Microcontroller and close the desired circuit on the board. Microcontrollers do not have amazing capabilities and their processing power is limited. These chips are used for specialized tasks such as controlling toys, medical devices, office machines, motors, home electronic devices and remote controllers.