افشین رشید
اُستادیار ؛ عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی واحد علوم و تحقیقات تهران
654 یادداشت منتشر شدهLindemann Change (Change Structure) of Carbon Nanostructures, Nanoelectronic Devices and Devices
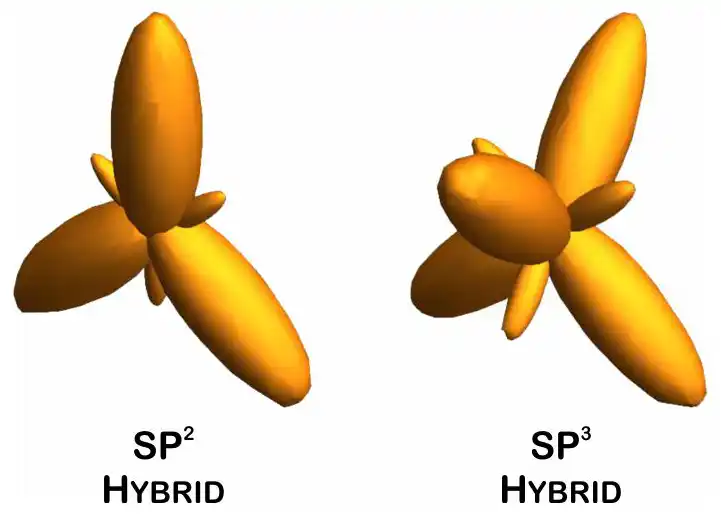
Note: This division of nanomaterials (nanostructures) is not an apparent and worthless division. These three types of nanostructures have fundamental differences from each other, both in terms of synthesis and production, and in terms of properties and applications. In general, the electrical, optical, magnetic, surface, etc. properties of these three structures are fundamentally different from each other, and of course their applications are also different.
The main basis of nanotechnology is the use of materials. Every material in space has three dimensions: length, width and height. If at least one of these three dimensions in a material is in the nanometer range, it is called a material, a nanostructure. There is no accepted definition of the nanometer range, but a more acceptable definition is a range between one and one hundred nanometers. Nano Carbon Nanopowder is a form of carbon nanoparticles. Nano Carbon Nanopowder is produced by using low-temperature physical exfoliation of natural carbon (the material used in pencils) in deionized water. This means that Nano Carbon Nanopowder is exposed to temperatures below 650 degrees Celsius. The final material is stable at room temperature and shows no signs of flammability.
In nanoscience and nanoelectronics, nanocarbon has many applications. Carbon is one of the amazing elements of nature that is found in four different forms of graphite, diamond, coal and other carbon forms in nature. All of these four forms are solid and in their structure, carbon atoms are perfectly and regularly arranged next to each other. Carbon is one of the most important elements in nature and its numerous applications in human life confirm this point well. For example, steel - which is one of the most important engineering alloys - is obtained by dissolving about two percent of carbon in iron; by changing the percentage of carbon by only a few hundredths of a percent, different types of steel can be obtained. "Organic chemistry" is also a science that studies compounds containing "carbon" and "hydrogen", and polymer engineering is based only on the element carbon. Carbon is found in four different forms in nature, all of these four forms are solid and in their structure, carbon atoms are perfectly and regularly arranged next to each other.
Example of carbon nanostructures
Carbon-based nanotransistors are very serious candidates to replace conventional silicon transistors. Transistors are the main electronic components used as amplifiers in analog circuits or electronic switches in digital circuits. And their development is the key to nanoelectronics in the field of production and monopolization (nanochips) in the field of military and biological industries. Transistors and integrated circuit manufacturing technology have become the most common based on them, namely CMOS technology, in the micro and nanoelectronics industry. This industry and integrated circuit manufacturing technology, this advantage of nanoelectronics in reducing the size of transistors and the number of transistors used in each chip, is doubled. The reduction in the dimensions of transistors leads to increased speed and reduced power losses.
Conclusion:
This division of nanomaterials (nanostructures) is not an apparent and worthless division. These three types of nanostructures have fundamental differences from each other, both in terms of synthesis and production, and in terms of properties and applications. In general, the electrical, optical, magnetic, surface, etc. properties of these three structures are fundamentally different from each other, and of course their applications are also different.