افشین رشید
اُستادیار ؛ عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی واحد علوم و تحقیقات تهران
654 یادداشت منتشر شده(Nanoelectronics - Plasmonic) and the approach of nanoplasmonic technology towards the assembly of optical nanoelectronics circuits

Note: In nanoelectronics, surface plasmon intensification is the coordinated and cumulative oscillations of metal electrons that are excited by radiation.
In electronic science, the topic of nano revolves around (nano memories, nano chips and fast nano chips and nano electronic components) with less weight and more efficiency. Nanotechnology, knowledge, engineering and technology on a nano scale, or in other words, studying the application of very small objects and their use in all fields of science such as chemistry, biology, electronics; Material science and engineering. The history of nanotechnology describes the development of concepts and experimental work done in the field of nanotechnology. Although nanotechnology is one of the recent advances in scientific research, the development of its fundamental concepts has taken place over a long period of time. The condition of oscillation is that the frequency of the photons of the radiated beam becomes the same as the natural frequency of the surface electrons (which is to overcome the central nuclear force). The resonance of surface plasmons in structures with nanometer dimensions is called Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. Localized surface plasmons are non-emissive excitation of conduction band electrons of metal nanostructures to which an electromagnetic field is coupled. Plasmonic waves are generated by using the scattering problem from a conductive nanoparticle whose dimensions are below the wavelength of the electromagnetic field of the excitation beam. These nanostructures consist of metal and dielectric, whose dimensions are below the excitation wavelength (the wavelength of the radiation that causes the excitation of plasmonic waves). Plasmonic is based on the process of interaction between electromagnetic waves and conduction electrons in metals with nano dimensions. Analytically, the reason is the rapid drop in the energy of electrons passing through metals, and it was concluded that this energy is spent on the cumulative movement and oscillation of the free electrons of the metal and called it plasmon.
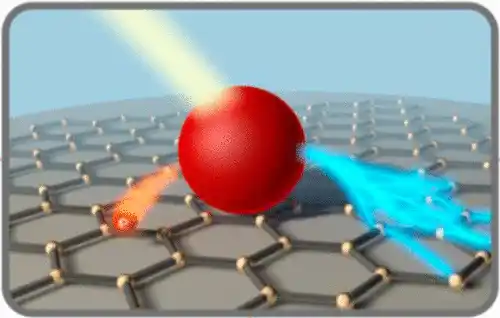
One-dimensional localized surface plasmon nanostructures can be used for electronic connections, while there is no such application for zero-dimensional and two-dimensional nanomaterials. The main basis of nanotechnology is the use of materials. Every material in space has three dimensions: length, width and height. With the approach of technology towards the accumulation of opto-electronic circuits, manufacturing problems and phenomena that helped prevent further compression of the structure, caused the use of plasmonic structures and plasmonic waves to be investigated and used. These nanostructures consist of metal and dielectric, whose dimensions are below the excitation wavelength (the wavelength of the radiation that causes the excitation of plasmonic waves).
Conclusion :
In nanoelectronics, surface plasmon amplification is the coordinated and cumulative oscillations of metal electrons excited by radiation.