افشین رشید
اُستادیار ؛ عضو هیات علمی دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی واحد علوم و تحقیقات تهران
651 یادداشت منتشر شدهCellulose Nano Particles is Known as the Most Abundant Biopolymer on Earth

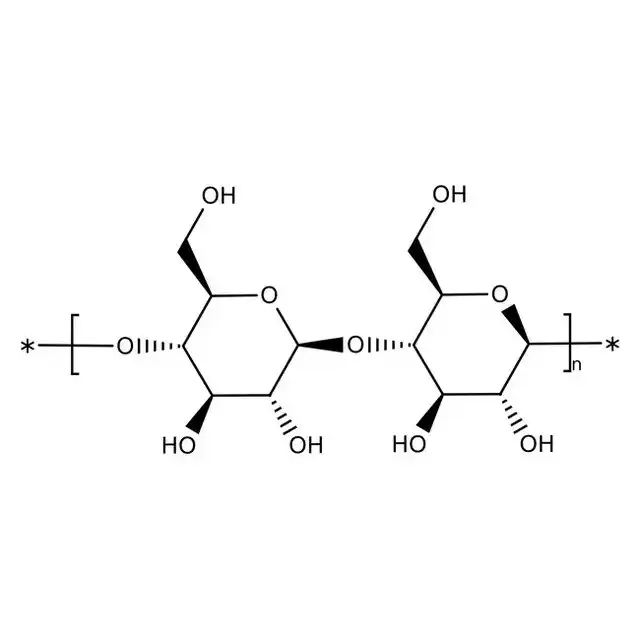
Note: Cellulose is a molecule made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and is found in the cellular structure of almost all plant matter. This organic compound, which is considered the most abundant substance on Earth, is even excreted by some bacteria.
Cellulose is known as the most abundant biopolymer on Earth. It is a complex carbohydrate or polysaccharide consisting of hundreds to thousands of glucose molecules linked together to form chains. Cellulose is made up of β-(1→4) glycosidic bonds between D-glucoses. In contrast, glycogen and starch are made up of α-(1→4) glycosidic bonds between glucose molecules. The bonds in cellulose make it a linear chain polymer. The hydroxyl groups on the glucose molecules form hydrogen bonds with oxygen atoms, holding the chains firmly in place and giving the fibers high tensile strength.
The use of particles from the micro to the nanoscale provides advantages for various scientific fields, but since a large percentage of their atoms are located on the surface, nanomaterials can react very much and pose potential risks to humans. Nanoparticles are of great interest both in industry and in the natural sciences due to their wide application. While natural materials have constant physical properties regardless of size, the size of a nanoparticle determines its physical and chemical properties. Therefore, the properties of a material change as its size approaches the nanoscale and the percentage of atoms on the surface of the material becomes significant. An important feature of all nanostructures is that the number of surface atoms in them is greater than the number of bulk atoms. This ratio increases with decreasing nanoparticle size. Therefore, the size of the nanoparticle is its important feature. The range of change in the activity of nanoparticles depends on the nature and shape of the nanostructure. However , if the energy of the nanoparticle field is comparable to the energy of the electromagnetic radiation and if significant changes occur in the irradiated material within a certain wavelength range due to chemical reactions, the activity of nanoparticles as small as 100 nm will be significant. The atoms on the surface of the nanoparticles are not compensated in terms of energy. In general, the results of the growth of the energy of the nanoparticle can be expressed as the total energy of the atoms on the surface of the particle. The freedom of movement of the atoms on the surface of the nanostructures is limited, and only vibrational movements and electron motion are possible. These two electrokinetic reactions are interdependent because the displacement of the electron clouds of the atoms inevitably changes the vibrational frequencies of the bonds of the atoms of the nanoparticles . On the other hand, the change in the location of the valence electrons in the bonds changes the polarity of the bond and the objects called the supermolecule . In this case, the transfer of the electron to a higher energy level becomes possible.
Conclusion:
Cellulose is a molecule made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and is found in the cellular structure of almost all plant matter. This organic compound, considered the most abundant substance on Earth, is even excreted by some bacteria.