منوچهر عابدی راد
محقق رشته منابع طبیعی و محقق تاریخ جنوب ایران (لارستان ) و خلیج فارس
30 یادداشت منتشر شدهPh.D. Research Proposal
Ph.D. Research Proposal
Research Title:
Utilization of Urban Runoff in Micro-Catchments of Arid and Semi-Arid Regions for the Sustainable Development of Household Green Spaces ، and the maintenance and development of neighborhood and urban green spaces”،،،،: A Low-Cost, Gravity-Based, Energy-Free System Design Approach
Applicant:
Manouchehr Abedi-Rad
National ID: @@@@@@31
Student ID: 37890112354–ZP365
1. Introduction and Problem Statement
Water scarcity is one of the major challenges of the 21st century, particularly in countries located within the Earth’s arid belt. Nations such as Iran, Afghanistan, the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Yemen, and many others in the Middle East face decreasing renewable water resources and increasing demands from urban, agricultural, and industrial sectors. Climate change, erratic precipitation patterns, and urban sprawl have exacerbated this crisis.
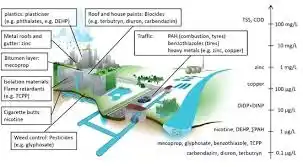
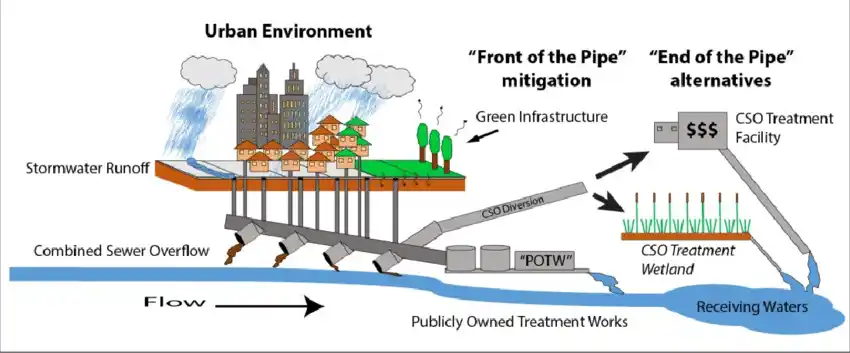
Urban runoff, which is often discharged without use, can, with a scientific and engineering approach, be transformed into a valuable resource for groundwater recharge, urban green space development, and urban heat mitigation. Implementing low-cost, gravity-based, energy-free systems for the collection and use of this resource could be a practical solution in urban water management.
2. Research Objectives
• To design simple, low-cost, energy-free models for the utilization of urban runoff.
• To increase per capita household and neighborhood green spaces in arid and semi-arid areas.
• To enhance the resilience of cities against water scarcity and climate-induced heat.
• To propose a locally adaptable model for Middle Eastern and North African countries with similar climates to Iran.
3. Main Research Questions
• How can seasonal urban runoff be effectively utilized using micro-catchments?
• What gravity-based and energy-free systems perform best for collection, primary filtration, and use of urban runoff?
• At what scale can this model be implemented in low-income urban areas?
• What social, cultural, or administrative obstacles may hinder the implementation of such projects?
4. Research Methodology
• Climate Data Analysis: Examination of precipitation and temperature patterns in low-rainfall regions of Iran, with a focus on the southern provinces.
• System Modeling and Design: Use of water engineering software to design collection and utilization systems for urban runoff.
• Field Studies and Pilot Implementation: Experimental implementation in one or more sample cities (e.g., Lar, Shiraz, or Bandar Abbas).
• GIS and Satellite Imaging: Identification of potential micro-catchments suitable for runoff harvesting.
• Economic and Socio-Environmental Evaluation: Assessment of project costs and benefits from economic, social, and environmental perspectives.
5. Significance and Innovation
This research has immediate and broad applicability in water-scarce countries and contributes to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, especially SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). Its emphasis on natural forces (gravity) and elimination of electricity needs makes it a feasible and low-cost option for underdeveloped areas.
6. Researcher’s Background
Manouchehr Abedi-Rad, M.Sc. in Natural Resources from Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, has over 30 years of experience in water, soil, and rangeland resource management. He has collaborated extensively with Dr. Seyed Ahang kowsar on flood spreading, artificial aquifer recharge, and integrated watershed management. His work includes academic publications, scientific papers, and international experience with the FAO and global forums.
7. Conclusion
This study provides a scientific and operational response to one of the region’s most pressing environmental and urban challenges. With appropriate academic guidance and institutional support, it can serve as a model for other nations facing similar issues.
References
1. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. (n.d.). Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation. Retrieved from https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/water-and-sanitation/
2. EPA. (n.d.). Green Infrastructure in the Semi-Arid West. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/green-infrastructure/green-infrastructure-semi-arid-west
3. ResearchGate. (n.d.). Green infrastructure: An ally to improve urban runoff management in semi-arid areas. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356913463_Green_infrastructure_An_ally_to_improve_urban_runoff_management_in_semi-arid_areas
4. ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Rainwater utilization from roof catchments in arid regions: A case study. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140196314001645
5. MDPI. (n.d.). Delineating the Potential Areas of Rainwater Harvesting in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/15/20